The government introduced the new GST Return SAHAJ form (GST RET 2) for taxpayers with certain conditions. This certain points will be applicable to the taxpayers having a turnover up to 5 crores and is optional for them to file. The GST SAHAJ RET 2 form has been filing on a trial basis since 1st July 2019. and stable basis will go live from April 2020 as per the recommendations by GST council members.
The GST SAHAJ form (RET 2) has to be filed quarterly and by the taxpayers dealing in business to customers transactions. The taxpayers filing the new RET 2 form can also file Nil returns via SMS. The HSN based turnover taxpayers also have the optional feature to adhere.
The taxpayers filing the GST SAHAJ return form doesn’t require to declare the capital input. However, Declared Inward supply on which RCM apply is to be given under the form.
The GST Council has issued the following 3 new, simplified GST Forms:
- Normal (RET-1)
- Sahaj (RET-2)
- Sugam (RET-3)
Filing Procedure of GST Return Form Sahaj RET 2 Quarterly
The GST Sahaj (RET-2) form has been divided into 7 parts.
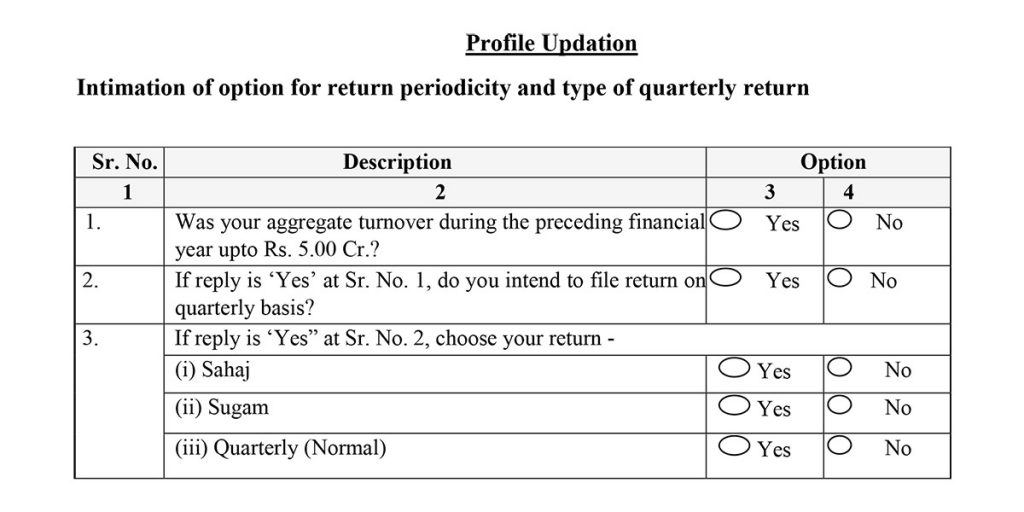
Profile Updation
Intimation of option for return periodicity and type of quarterly return
In this section, the forms want to ascertain the total turnover of the taxpayer with the help of question while further asks for the intention of the return filing individual to clarify his wish to file the form and if yes, then which of the form under these newly introduced forms namely (Sahaj, Sugam & Quarterly) he intends to file.
Also, there are important notes to be taken care of while filing the form and details input which are clarifying the points.
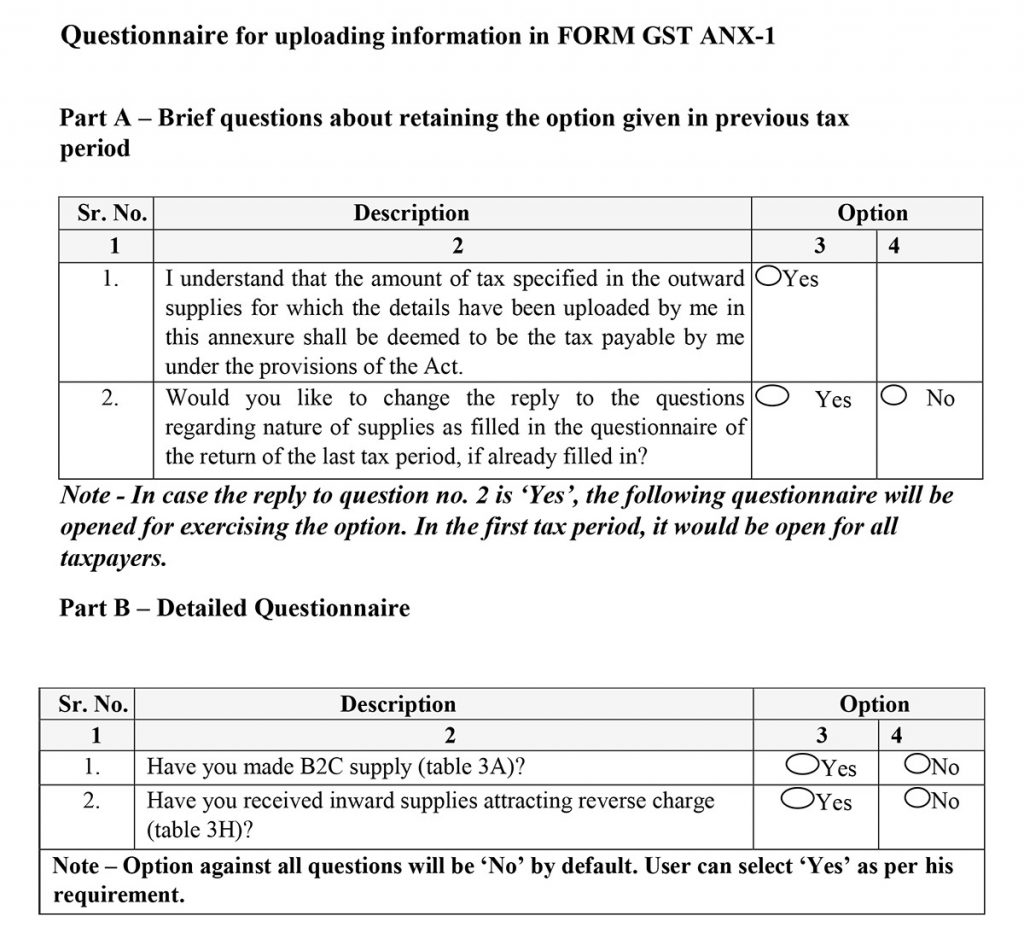
Questionnaire for Uploading Details in GST Sahaj ANX-1 Form
The further questionnaire asks the taxpayer to fill the details regarding the previous tax period under which the form will ask a certain question and in case the individual selects the 2nd option then he is liable to answer the second part of the questionnaire which is in a detailed manner.
GST Sahaj ANX-1 for Outward and Inward Supplies
Details of Outward Supplies And Inward Supplies Attracting The Reverse Charge
Further, the Annexure 1 will require some basic details of the taxpayers including trade name, ARN and other mandatory information about the form.
In the second part, there is 3 subsection which is based on “Details of outward supplies and inward supplies attracting reverse charge”. These subsections would require details on Supplies made to consumers and unregistered persons (Net of debit/credit notes ) and Inward supplies attracting a reverse charge.
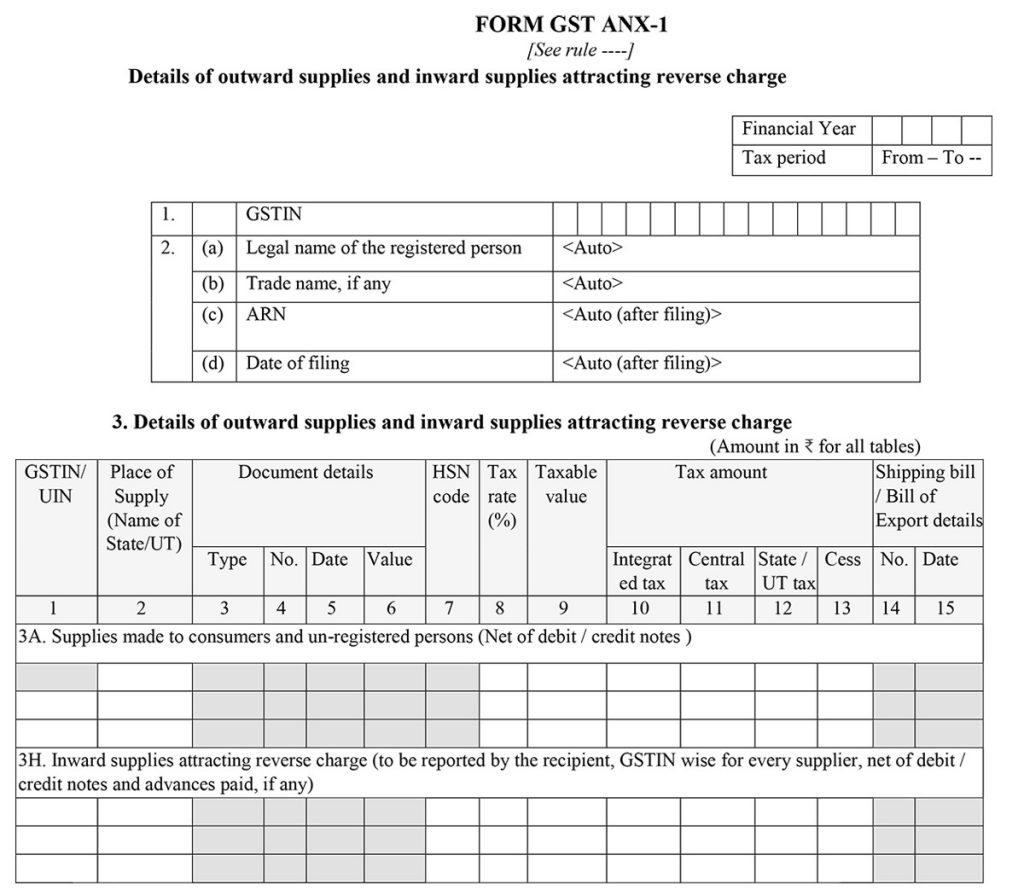
Sahaj GST ANX-2 Auto Drafted Inward Supplies Form
Details of Auto- Drafted Inward Supplies
Here in the Form GST ANX 2, there will basic details asked which will be Details of auto- drafted inward supplies. It includes 4 parts with basic details, Inward supplies received from a registered person (other than the supplies attracting reverse charge), Summary of the input tax credit.
Further, there will be a single page questionnaire regarding the Option to file ‘Nil’ return with the question of intention to file the NIL return by the taxpayer.
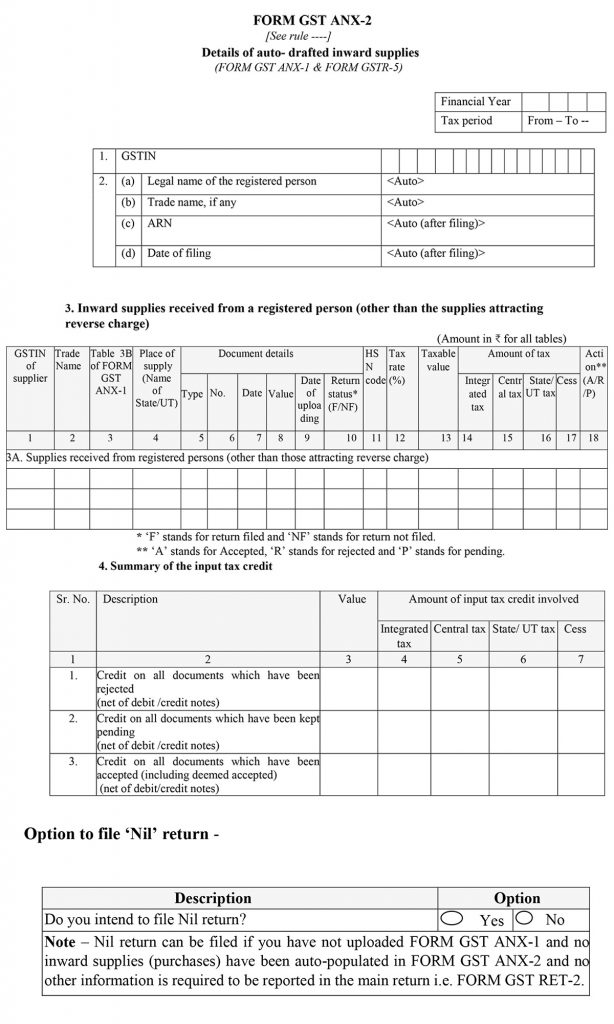
GST Sahaj Quarterly Return RET 2 Form Format
Quarterly Return (Sahaj Form)
The next in line of the GST Sahaj form is the quarterly return part which consists of 9 subsections with having basic details to be filed at the top. After it, there is a 3rd part for Summary of outward supplies, inward supplies attracting reverse charge and tax liability for the taxpayer to file. Coming to the 4th part is Summary of inward supplies for claiming the input tax credit (ITC).
Now discussing the 5th part of the form will ask for the Amount of TDS and TCS credit received in electronic cash ledger. The 6th part requires Interest and late fee liability details. While in the next part there is the discussion of Interest and late fee liability details, Payment of tax, Refund claimed from electronic cash ledger. After filing all the details one has to verify the information by self-attesting
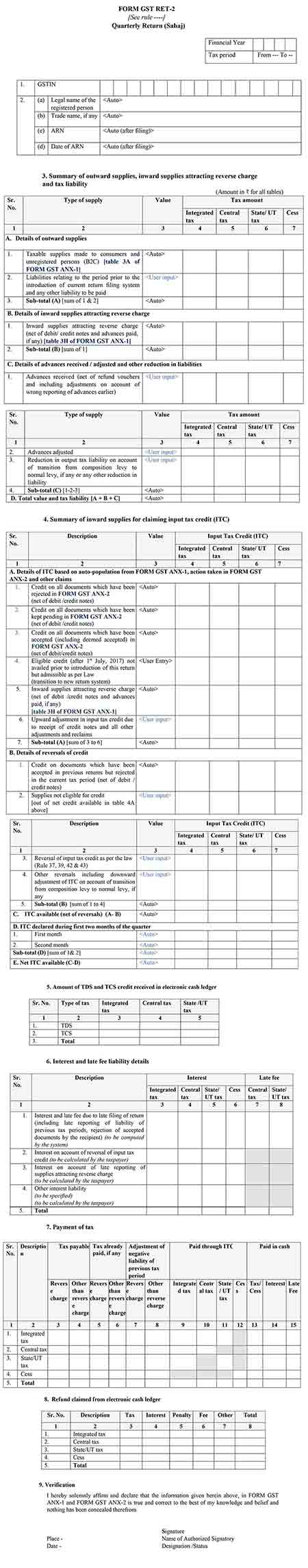
Amendment to Form GST Sahaj RET 2 (Including Form GST ANX-1)
The questionnaire based on FORM GST ANX-1A i.e. Amendment to FORM GST ANX-1
The question set asks the intention of the taxpayers if he wants to amend the B2C supply details and amend inward supplies attracting reverse charge (Table 3H).
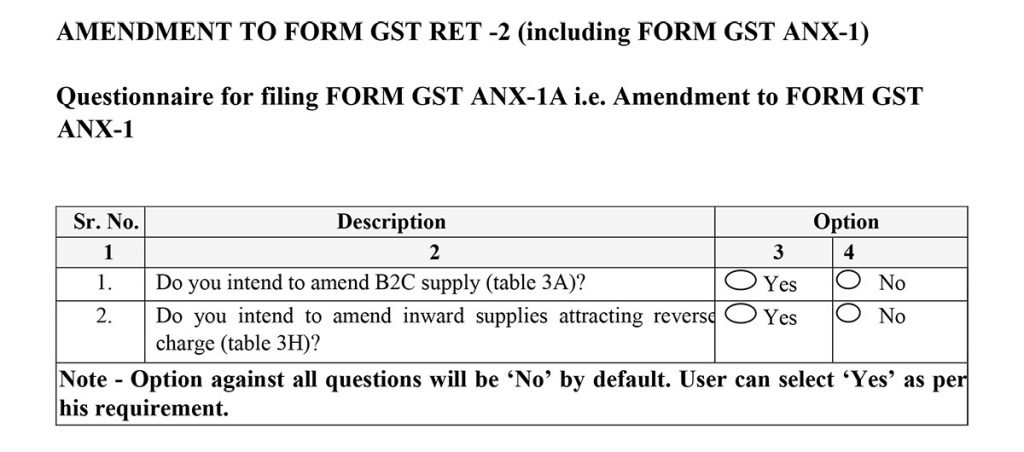
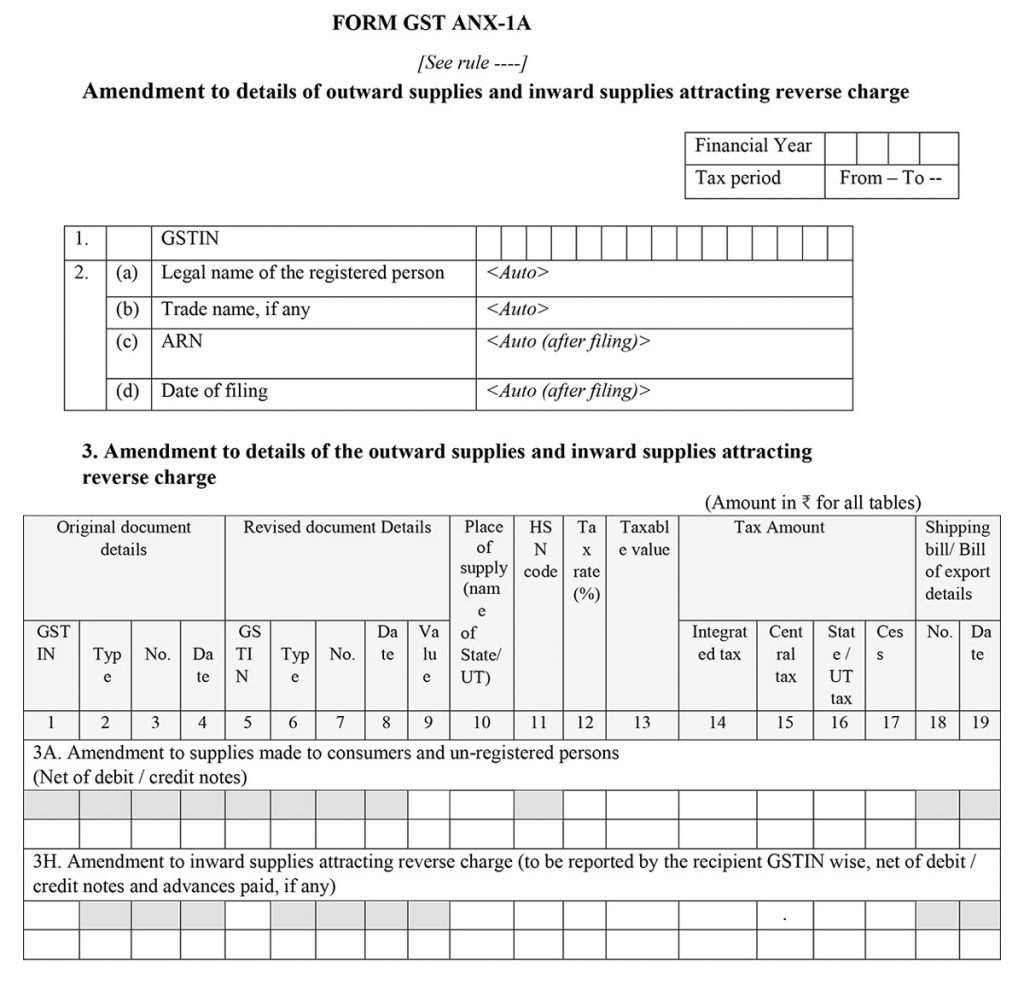
GST ANX-1A Amendment Details of Outward and Inward Supplies
The form is for an amendment to details of outward supplies and inward supplies attracting reverse charge and the amendment to details of the outward supplies and inward supplies attracting a reverse charge.
Also, there are sub-parts of the 3rd points in which amendment to supplies made to consumers and unregistered persons and the amendment to inward supplies attracting reverse charge (to be reported by the recipient GSTIN wise, net of debit/credit notes and advances paid, if any).
Form GST RET 2A Quarterly Return (Sahaj Form) Format
Amendment to quarterly return (Sahaj Form)
In the next part, there comes the Amendment to quarterly return (Sahaj Form) required details. In this form, a total of 7 parts with further subsections within them. Starting with the basic details of the trade name and registration details with ARN.
Coming to the 3 subsections, there are details required for amendment in summary of inward and outward supply attracting tax liability and reverse charge. In the 4th section, there is Amendment to the summary of inward supplies for claiming the input tax credit (ITC) related details which has to be inserted by the taxpayer.
In the 5th and 6th section, there are details related to the interest on tax and the payment of taxes along with the late fees. Finally, in the last part, there is self-attested verification to be done from the taxpayer.

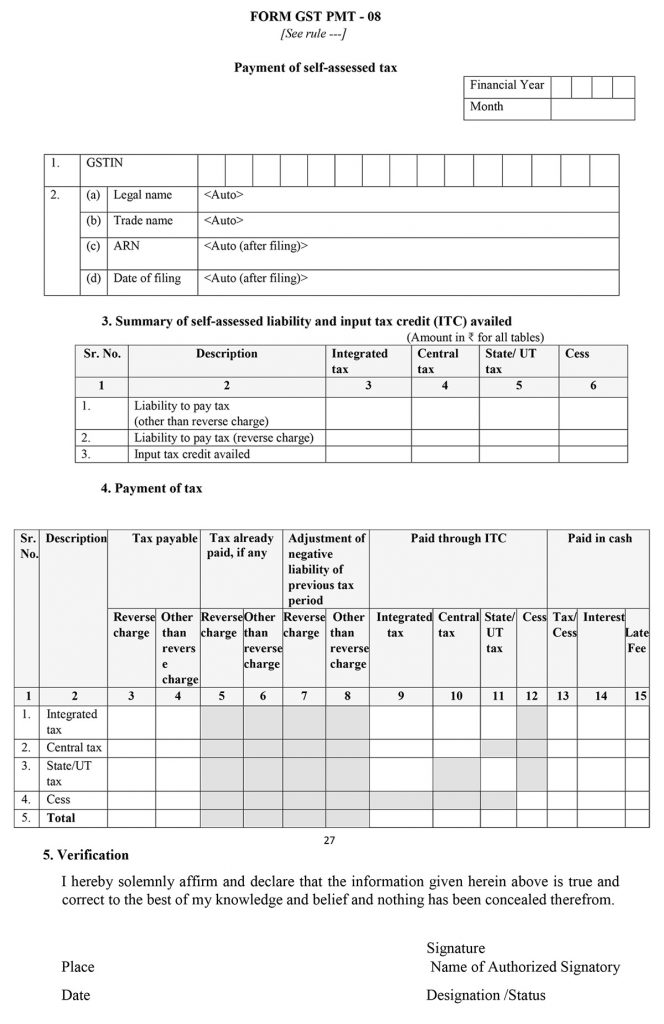
GST PMT 08 Payment of Self-assessed Tax Form
Payment of self-assessed tax
Finally, there comes the payment form also considered as the challan which includes 5 subsections. First of all, there are basic details including the trade name and the ARN number has to be filed. In the other subsection, there are details required such as Summary of self-assessed liability and input tax credit (ITC) availed and the tax payment details.
Finally one has to verify the payment details in the self-attested verification form at last.
Here we have debriefed complete details and form structure of the GST Sahaj form recently released by the government of India.
Read Also: Full Compare New GST Return Normal, Sahaj & Sugam Forms