
What is Income Tax?
Tax is a pivotal arm for good governance of a state or nation.
There are different types of taxes and they can all be categorized into two main groups i.e Direct tax and Indirect Tax.
A direct tax is levied on the income or profit of an individual. Income tax is an example of direct tax. Indirect tax is levied on goods and services.
Income tax due date comes every year in March ending must be followed strictly for safeguarding financial interest.
A popular example in this regard would be the GST or the VAT.
Like all taxes, accrues from Income Tax also constitute a good portion of the country/state treasury. In addition to these Income Tax also acts as a fiscal deficit stabilizers as well as minimizing impact of Global Economic Cycles.
Types of Income Tax
Income Tax is further subdivided into three more categories based on the category of payee and time of payment.
These are:
- 1. TDS (Tax Deducted at Source)
- 2. Advance Tax
- 3. Self-Assessment Tax
1. Tax Deducted at Source (TDS)
TDS, as it is commonly known, is collected at the income source itself. The tax is paid by a third person/corporation who/which happens to be the source of income for the taxpayer.
The other person/corporation must, however, abide by the prevalent IT laws. TDS is an ideal mechanism for the government to ensure timely Income Tax payment as well as curb tax evasion.
2. Advance Tax
Also referred to as ‘pay as you earn tax’ in contrast to the scheduled annual tax payment tax procedures, Advance Tax is paid on a Presumptive basis.
Taxpayers, Businesses, Salaried Individuals and freelancers with tax liabilities greater than Rs 10,000 for the current Financial Year are needed to pay advance tax in four installments throughout the financial year in which they earn income.
The taxpayers need to pay Advance Tax as per the following table:
Advance Taxes of Income Tax for FY 2018-19 & AY 2019-20
| Due Date | Pay Advance Tax |
|---|---|
| On or Before 15th June | 15% |
| On or Before 15th September | 45% |
| On or Before 15th December | 75% |
| On or Before 15th March | 100% |
For businesses who have opted for Presumptive Taxation Scheme 100% of advance tax is payable by 31st March.
3. Self-Assessment Tax
This is the balance or remaining tax paid by an individual or taxpayer after taking into account the TDS and Advance Tax.
What is meant by Assessment year and Financial Year?
Financial Year is the current working year in which an individual or corporation earns income. The Assessment Year is on the other hand the succeeding year in which evaluation of the previous year’s income has to be made.
Assessment Year involves:
- Income Evaluation.
- Paying Taxes on the evaluated income as per the rate(progressive) and time ( regular or periodical or on an occasional) notified by the IT Department.
- For FY 2018-19, the AY is 2019-20.
- The last date to file the tax return (ITR) for the financial year 2018-19 is 31st July 2019.
File Your IT Return By Fastest Income Tax Filing Software
100% SECURE | TIME SAVING | EXPERT SUPPORTFile It Now & Download Free Demo
Income Tax Returns (ITR)
ITR are forms that are mandatorily filled by individuals whose annual income greater than a pre-set threshold limit set by the Finance Department.
It details the individual’s gross income from various sources and respective tax paid by the individual taxpayer on the gross income. It also details the refund claims as per the rules set by the Finance and IT Department.
In simple terms, ITR forms are taxpayers statement detailing his/her earnings regular income (wages), interest, dividends, capital gains, or other profits, the total tax paid on earnings and the appropriate refunds to be repaid to him/her by the Government.
As per the Central Board of Direct Taxes, individual taxpayers need to file only 6 of the 9 ITR Forms.
These include:
- ITR-1
- ITR-2
- ITR-2A
- ITR-3
- ITR-4
- ITR-4S
The remaining three forms are to be filed by companies and firms alone:
- ITR-5
- ITR-6
- ITR-7

Form ITR-1
Also known as the Sahaj Form, ITR-1 has to be filed by individual taxpayers alone. Individuals belonging to any of the following groups need to file ITR-1 Form.
- Individuals who are Salaried or claim Pension.
- Individuals whose only source of income includes a single housing property
- Individuals with income sources like fixed Deposits, Investments, Shares etc
- Individuals with no income sources outside India.
- Individuals whose net agriculture income is less than Rs 5,000.
- Income from other sources (excluding winning from lottery and income from race horses, income tax under section 115BBDA or Income of nature referred to in section 115BBE)
Form ITR-2
This form was introduced during the assessment year 2015-16 for use by Hindu Undivided Family (HUF) or any individual. The following individuals/taxpayers can file ITR-2 Form.
- Those individuals eligible to file Sahaj () and
- Those who claim no income source under the head “profits or gains of business or profession”.
Form ITR-3
ITR 3 Form is for use by a Hindu Undivided Family or an individual
- Who is not qualified to file Sugam (ITR-4)and
- claims income under the head “profits or gains of business or profession”
Form ITR-4
Also known as Sugam, ITR 4 Form is for use by HUF/ individual / Partnership Firm whose total income subsumes:
- Business income evaluated in reference with special provisions mentioned in section 44AD and section 44AE of the Act for computation of business income; or
- Professional income evaluated in reference to special provisions of sections 44ADA; or
- Salary/ Pension; or
- Income from One House Property (excluding cases where a loss is brought forward from previous years); or
- Income from other sources (excluding windfalls like lotteries or horse racing)
Form ITR-5
ITR-5 is for firms, LLPs, AOPs (Association of persons) and BOIs (Body of Individuals). Further, it is also meant for an artificial juridical person referred to in section 2(31)(vii), cooperative society and local authority. ITR-5 can be filed both online (under digital signature) and offline.
Form ITR-6
ITR 6 can be used by companies claiming exemption on income from property held for charitable or religious purposes under section 11.
Form ITR-7
ITR 7 Form can be used by persons as well as companies which are required to furnish return under:
- section 139(4A) or
- section 139(4B) or
- section 139(4C) or
- section 139(4D) or
- section 139(4E) or
- section 139(4F).
Important Income Tax Return Filing Due Dates for FY 2018-19 (AY 2019-20)
The income tax due date 2018 for both the categories of taxpayers are specified below:
Extended Due Date File Income Tax Return Form For FY 2018-19 AY 2019-20
CBDT has today announced to extend the due date for filing of Income Tax Returns (ITR) to 31st August 2019 only for taxpayers who were supposed to file their Returns by 31.07.2019. Notification by CBDT

As per the section 234F of the Income Tax Act, 1961, the late payment of return will attract late fee charges and the late filing fee is required to be paid ahead of the furnishing income tax return.
Some changes are made to the FY 2018-19 and are listed below:
-> Reduced Tax Rate
The taxpayer whose income ranges from 2.50 lakh to 5 Lakh has to pay tax at 5% instead of 10% before.
-> Rebate
In FY 2016-2017, for a taxpayer with annual earning up to Rs. 5 lakh, the allowed rebate was Rs. 5,000. Now, the residential individual will get a rebate of Rs. 2,500 with an annual income of up to Rs. 3.50 Lakh.
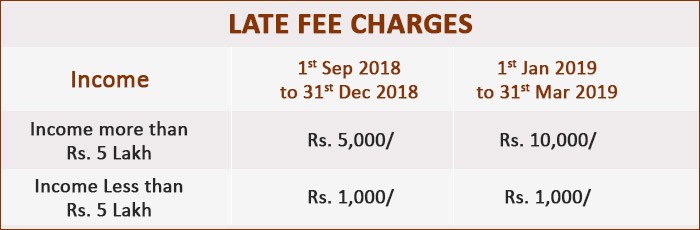
-> Late Fee
If the taxpayer does not file income tax return before 31st August 2018 which is the due date, then he/she has to pay a late filing fee under section 234F. This late fee is chargeable ahead of furnishing Income Tax return.
-> Limit In Donations
Previously, cash donations of up to Rs. 10,000 was permitted in terms of deduction. This limit has been reduced to Rs. 2,000 starting from FY 2018-19.
-> Section 194-IB For HUF and Individuals Paying Rent Exceeding Rs 50,000 a Month
HUF and Individuals who pay Rs. 50,000 and more in rent per month, 5% TDS will be deducted on such rent amount.
-> Cess
In order to increase the funds for education purpose, Secondary and Higher Education Cess which is 1% and Education Cess which is 2% is replaced by the Health and Education Cess which is 4% now.
-> Income from Salaries
From the salaried income, a standard deduction at a fixed price of Rs. 40,000 for reimbursement and Transport of various medical spendings will be permitted. This deduction is also exercisable to Pensioners who presently do not obtain those benefits.
Moreover, the medical reimbursement advantages in hospitalization case will be available along with the standard deduction as mentioned above.
